Table of Contents
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in the field of dentistry, providing valuable insights into oral health. These diagnostic images allow dentists to identify and diagnose various dental conditions that may not be visible during a regular dental examination.
By using X-rays, dentists can detect dental issues at an early stage, leading to prompt treatment and prevention of further complications.
Definition of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays, also known as dental radiographs, are images of the teeth and surrounding structures captured using X-ray technology.
These images provide detailed information about the teeth, bones, and soft tissues of the mouth, helping dentists to evaluate oral health conditions accurately.
Types of Dental X-Rays
There are different types of dental x rays, each serving a specific purpose. The most common types include:
1. Bitewing X-Rays
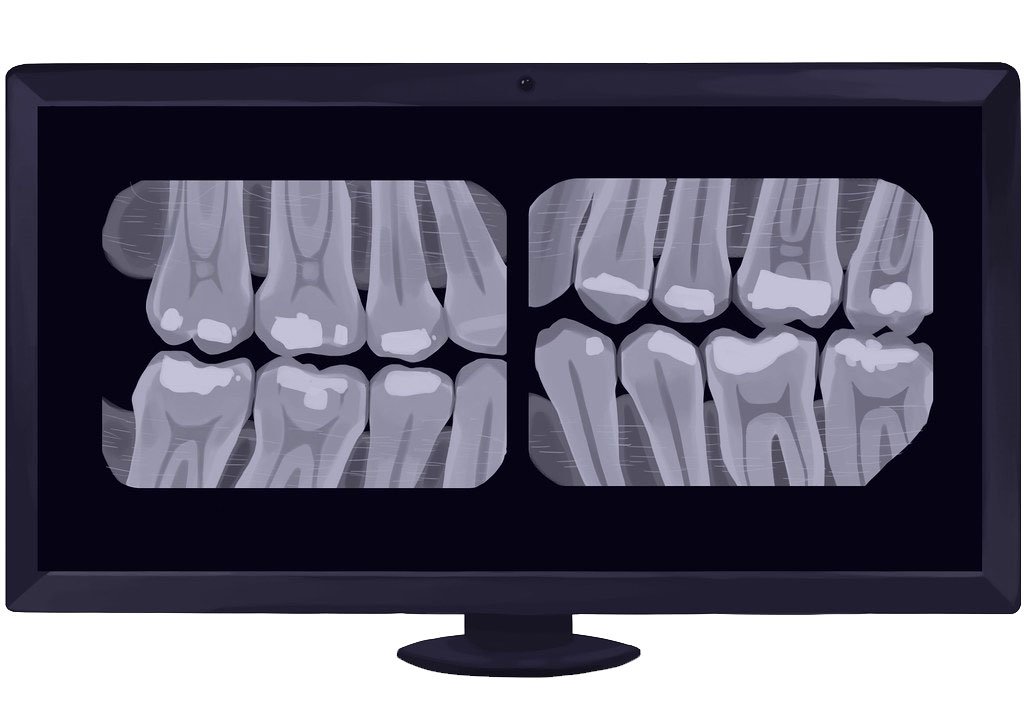
Bitewing x-rays are used to detect cavities between the teeth and evaluate the fit of dental restorations, such as fillings or crowns. These x-rays show the upper and lower teeth in a single image.
2. Periapical X-Rays
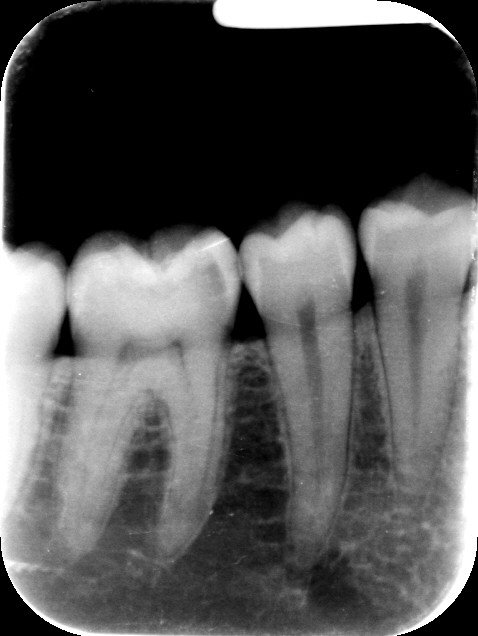
Periapical x-rays focus on individual teeth and provide a detailed view of the entire tooth, from the crown to the root. These x-rays help dentists assess the health of the tooth structure and surrounding bone.
3. Panoramic X-Rays
Panoramic x-rays capture a wide view of the entire mouth, including all the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. These x-rays are useful for evaluating overall dental health, detecting impacted teeth, and planning orthodontic treatment.
4. Cone Beam CT Scan
A cone beam CT scan is a specialized type of x-ray that provides a three-dimensional view of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. This type of x-ray is commonly used for implant planning and oral surgery.
5. Orthodontic X-Rays
Orthodontic X-rays, also called cephalometric X-rays, are used to assess the positioning of the teeth and jaws. These X-rays aid in planning orthodontic treatments and monitoring progress.
Overall, dental X rays are essential tools in dentistry, enabling dentists to diagnose and treat oral health issues effectively. By utilizing these diagnostic images, dental professionals can provide optimal care and maintain their patients’ oral well-being.
Why are Dental X-Rays Necessary?
Dental x rays play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of various dental conditions. Here are some reasons why dental x rays are necessary:
1. Detection of Tooth Decay
Dental x-ray can reveal early signs of tooth decay that may not be visible to the naked eye. By detecting decay in its early stages, dentists can provide appropriate treatment to prevent further damage to the tooth.
2. Evaluation of Tooth and Jaw Development
Dental x rays are particularly important for children and teenagers as they help dentists monitor the development of permanent teeth and identify any potential issues.
X-rays can also help evaluate the alignment of the jaw and detect any abnormalities that may require orthodontic treatment.
3. Identification of Dental Infections
X-rays can help dentists identify dental infections such as abscesses or infections in the root canal. These infections may not cause noticeable symptoms initially, but if left untreated, they can lead to severe pain and further complications.
4. Assessment of Oral Structures
Dental x-rays allow dentists to assess the health of the underlying structures in the mouth, such as the jawbone and the roots of the teeth. This helps in identifying issues such as bone loss, impacted teeth, or cysts that may require specialized treatment.
5. Planning for Dental Procedures
Prior to certain dental procedures, such as tooth extractions or dental implants, dentists rely on x-rays to assess the condition of the tooth and surrounding structures. This helps in planning the procedure and ensuring its success.
Safety Precautions
Dental professionals take several precautions to ensure the safety of patients during x-ray procedures. They use lead aprons and thyroid collars to protect the body from unnecessary radiation exposure.
Additionally, modern dental x-ray machines emit significantly lower levels of radiation compared to older models, making them safer for patients.
It’s worth mentioning that the radiation exposure from dental x-ray is comparable to the amount of radiation an individual receives from the natural environment over a few days or weeks.
Minimal Risk
The amount of radiation exposure from dental x-ray is relatively low. The risk of any adverse effects is minimal, especially when proper safety measures are followed.
The benefits of early detection and treatment of dental problems far outweigh the potential risks associated with x-rays.
Risk Factors
While the risks are minimal, certain factors may increase the potential for adverse effects. These include frequent exposure to x-rays, such as for individuals with extensive dental issues or those undergoing orthodontic treatment.
Pregnant women should also inform their dentist about their pregnancy as a precautionary measure, although the risk to the fetus from dental x-rays is extremely low.
In conclusion, dental x-rays are a safe and effective tool for diagnosing and treating oral health conditions. The minimal risks associated with x-rays can be further reduced by following proper safety precautions.
It is important for patients to communicate any concerns or specific circumstances, such as pregnancy, to their dental professional to ensure the highest level of safety during x-ray procedures.
Frequency of Dental X-Rays
The frequency of dental x-ray depends on various factors, including your age, oral health, and risk of dental problems. In general, new patients may require x-rays to establish a baseline for future comparisons.
For individuals with a history of dental issues, more frequent x-rays may be necessary to monitor their oral health.
As a guideline, most adults require dental x-rays every 1-2 years, while children and teenagers may need them more frequently due to their developing teeth and jaws.
The Procedure of Getting Dental X-Rays
Getting x-rays is a routine procedure that helps dentists diagnose oral health issues that may not be visible to the naked eye. Here is an outline of the steps involved in taking dental x-ray and what patients can expect during their appointment.
Step 1: Preparation
Prior to the x-ray, the dental technician will prepare the patient by providing a lead apron to protect the body from radiation.
The patient will also be asked to remove any jewelry or other metal objects that may interfere with the x-ray images.
Step 2: Positioning
Once the patient is ready, the dental technician will position the x-ray machine and adjust the patient’s head and body to capture the necessary images.
The technician may use a variety of tools, such as bite wings or a panoramic machine, depending on the type of x-rays needed.
Step 3: Taking the X-Rays
The dental technician will then take the x-rays by directing the machine to the specific areas of the mouth that need to be captured.
The patient will be asked to hold still and may be instructed to bite down on a piece of plastic or film to ensure the images are clear and accurate.
During this process, the patient may feel slight discomfort or pressure from the x-ray equipment, but it is generally painless and only takes a few seconds for each image.
Step 4: Review and Analysis
After the x-rays are taken, the dentist will review and analyze the images to assess the patient’s oral health. These images can reveal a variety of dental issues, such as cavities, gum disease, or abnormalities in the jaw or teeth.
Based on the findings, the dentist will discuss the results with the patient and develop an appropriate treatment plan if necessary.
In conclusion, getting dental x-rays is a straightforward procedure that involves preparation, positioning, taking the x-rays, and reviewing the images. Patients can expect a quick and painless experience that provides valuable insights into their oral health.
Interpreting Dental X-Rays: How Dentists Read and Interpret X-Ray Images
Dental x-rays are an invaluable tool for dentists to diagnose and monitor oral health conditions. These images provide a detailed view of the teeth, gums, and surrounding structures, allowing dentists to identify common findings such as cavities, bone loss, and impacted teeth.
Cavities
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are areas of decay on the tooth surface. When examining x-rays, dentists look for dark spots or areas of demineralization, indicating the presence of cavities.
By identifying cavities early, dentists can provide appropriate treatment to prevent further damage and preserve the tooth.
Bone Loss
Bone loss, also called periodontal disease, affects the supporting structures of the teeth. Dentists analyze x-rays to assess the level of bone loss around the teeth.
Signs of bone loss include a decrease in the height and density of the bone, as well as the presence of deep gum pockets. Early detection of bone loss is crucial in preventing tooth loss and maintaining oral health.
Impacted Teeth
Impacted teeth occur when a tooth fails to emerge fully or at all from the gum line. X-rays help dentists identify impacted teeth by revealing their position and orientation.
This is particularly important for wisdom teeth, which commonly become impacted. Dentists can then determine the appropriate course of action, such as extraction or orthodontic intervention.
When interpreting dental x-rays, dentists also consider other factors, such as the overall alignment of the teeth, the presence of dental restorations, and signs of infection or abnormalities.
By combining their expertise with the information provided by x-rays, dentists can develop personalized treatment plans to address any oral health issues.
The Future of Dental Imaging: Advancements and Innovations
Technological advancements in dental x-rays have revolutionized the field of dentistry, introducing digital x-rays as a superior alternative to traditional film x-rays. Digital x-rays offer numerous advantages, including enhanced image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and improved efficiency.
Furthermore, the future of dental imaging holds exciting prospects, with ongoing trends and innovations promising even more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
Advantages of Digital X-Rays
Digital x-rays utilize electronic sensors to capture images of the teeth and gums, which are then displayed on a computer screen. This technology offers several key advantages over traditional film x-rays:
- Enhanced Image Quality: Digital x-rays provide higher resolution and clarity, allowing dentists to detect and diagnose dental issues more accurately.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Digital x-rays require significantly less radiation compared to traditional film x-rays, making them safer for both patients and dental professionals.
- Improved Efficiency: With digital x-rays, there is no need to develop films, resulting in faster image acquisition and streamlined workflow in dental practices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Dental Imaging
The field of dental imaging continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development leading to innovative advancements. Some of the future trends and innovations in dental imaging include:
- 3D Imaging: Three-dimensional imaging techniques, such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), provide detailed and comprehensive views of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding structures, enabling more precise diagnoses and treatment planning.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms can analyze x-rays and assist dentists in detecting abnormalities, identifying cavities, and predicting potential oral health issues, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
- Minimizing Radiation Exposure: Ongoing research aims to further reduce radiation exposure in dental imaging, ensuring patient safety while maintaining diagnostic quality.
- Tele-dentistry: Advancements in technology allow for remote consultations and image sharing, enabling dentists to provide expert advice and collaborate with colleagues, even from a distance.
In conclusion, digital x-rays have revolutionized dental imaging, offering superior image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and improved efficiency.
The future of dental imaging holds exciting prospects, with advancements such as 3D imaging, AI-powered analysis, radiation reduction, and tele-dentistry promising even more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
Conclusion
Dental x-rays are an essential tool in modern dentistry. They provide valuable information that helps dentists detect and diagnose dental problems, plan treatments, and monitor oral health.
With advancements in technology and safety measures, x-rays are now safer and more efficient than ever before.
Regular dental check-ups, including x-rays when necessary, are crucial for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing dental issues from progressing. So, if your dentist recommends dental x-rays, rest assured that it is a necessary step in ensuring your oral well-being.
FAQs
-
What are dental x-rays?
Dental x-rays are a common diagnostic tool used by dentists to assess the health of your teeth, gums, and jawbone. They involve taking images of the oral structures to identify any potential issues that may not be visible during a regular dental examination.
-
Why are dental x-rays necessary?
Dental x-rays are essential for detecting problems such as tooth decay, gum disease, infections, and abnormalities in the jawbone. They provide a comprehensive view of your oral health, allowing dentists to make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans.
-
How often should dental x-rays be taken?
The frequency of dental x-rays depends on various factors, including your age, oral health history, and the presence of any ongoing dental issues. In general, adults may require x-rays every 1-2 years, while children may need them more frequently to monitor their dental development.
-
Are dental x-rays safe?
Yes, dental x-rays are considered safe. The amount of radiation exposure during a dental x-ray is minimal, and dentists take precautions such as using lead aprons and thyroid collars to further minimize radiation exposure. The benefits of dental x-rays in diagnosing and treating oral health conditions outweigh the potential risks.
-
Can pregnant women have dental x-rays?
While it is generally safe for pregnant women to have dental x-rays, precautions should be taken to minimize radiation exposure. Dentists may use lead aprons with thyroid collars to shield the abdomen and thyroid gland. It is important to inform your dentist if you are pregnant or suspect you might be.
Resources: ada